Regulatory Sequence Analysis Tools - Using RSAT-VM (Virtual Machine)
Jacques van Helden
Last update: 2024-03-01
1 Introduction
This tutorial explains how to install, configure and use a Regulatory Sequence analysis Tool (RSAT) server installed on a Virtual Machine (VM).
2 Prerequisite
To run this tutorial, you first need to install the VirtualBox software (https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads).
3 Importing the Virtual Machine archive (ova file)
3.1 Download
RSAT virtualboxes can be downloaded from the RSAT distribution site.
- Open a connection to any RSAT server (http://rsat.eu/).
- In the left-side menu, click on the Download link.
- Enter your coordinates and click GO. You will be redirected towards the download server.
- In the download Web site, the link virtual_machines.
- Download the version of your choice (current version:
rsat-vm-2018-05.ova).
3.2 Importing an appliance into VirtualBox
- In the VirtualBox menu, select the command File > Import Appliance ….
- In the import dialog box, click on the folder icon, and locate the
appliance file (
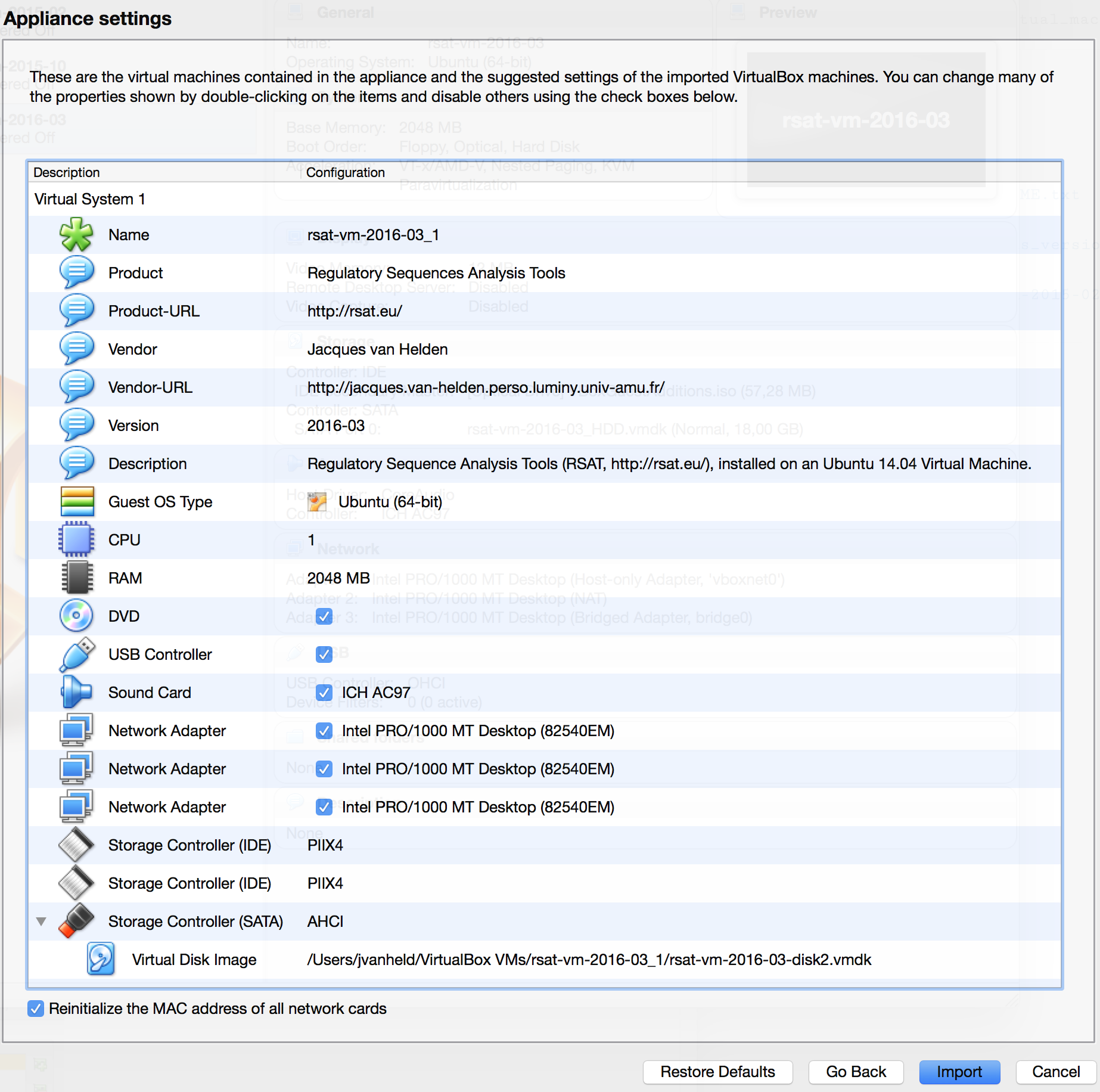
rsat-vm-2018-05.ova) that you downloaded from the RSAT Web site, and click on Continue. - In the Appliance settings dialog box (snapshot), check the option Reinitialize MAC address of all network cards.
- Click the Import button.
It should take a few minutes for VirtualBox to create a new instance of the virtual machine from the appliance.
4 Network configuration
The RSAT-VM is provided in a ready-to-use mode. However, you may need to adapt the configuration of your VirtualBox environment in order to obtain a correct behaviour of the VM.
Network configuration involves two aspects:
Configure VirtualBox to define the way(s) it will allow exchanges between virtual machines, the host machine (your computer) and the external world.
Configure each virtual machine, in order to define which types of access it will request from VirtualBox.
4.1 Host configuration: VirtualBox host-only adapter
The host-only adapter enables your computer (the “host”) to establish connections to the “guest” virtual machine. This is necessary if you want to use the VM as a Web server, or use command lines on a terminal (via ssh connection from the host machine).
Open the VirtualBox program.
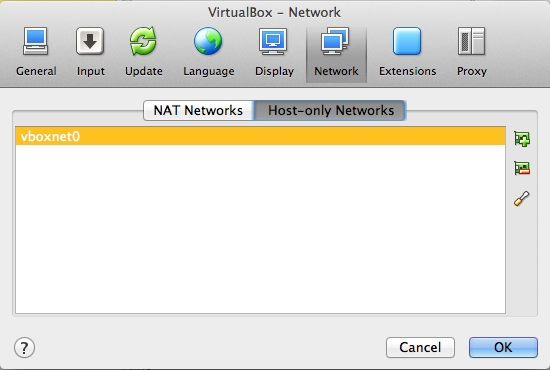
Open VirtualBox Preferences. Click on the Network option. Click on the tab Host-only Networks. Check if a host-only adapter is already installed. If not, create a new one by clicking the + icon on the right side (snapshot).
You should now see a host-only network named vboxnet0. Double-click on it to change its parameters.
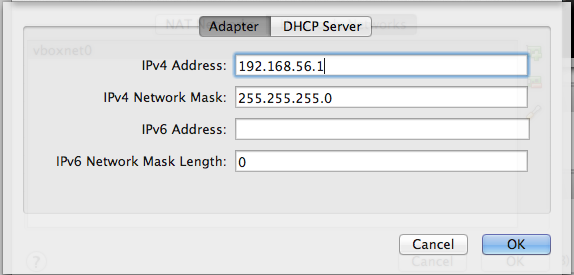
In the Adapter tab, set the parameters as follows (snapshot).
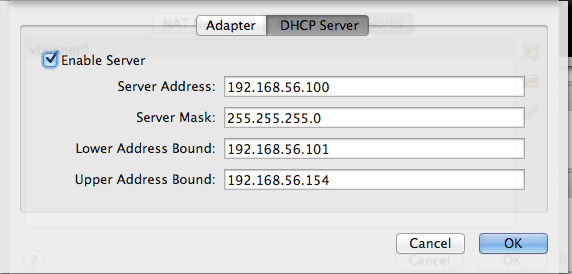
Parameter Value IPv4 Address 192.168.56.1 IPv4 Network Mask 255.255.255.0 IPv6 Address (leave this field blank) IPv5 Nework Mask length 0 In the tab DHCP Server, set the parameters as follows (snapshot).
- Check the option Enable Server
- Server Address: 192.168.56.100
- Server mask: 255.255.255.0
- Lower Address Bound: 192.168.56.101
- Upper Address Bound: 192.168.56.154
4.2 Network settings for the guest machine
VirtualBox supports various ways to connect the guest (virtual machine) to the network. The two first adapters are required for proper functioning of the RSAT VM. The third one is optional and should be enabled with caution.
Host-only network will enable the host machine (your computer) to access the virtual machine by HTTP (Web browser) or SSH (secure shell).
NAT will enable the communication from the virtual machine to the external world.
Optionally, a Bridged network might be configured in order to make your virtual machine visible from external computers.
4.2.1 Host-only network
This solution offers a good tradeoff between security and confort: your virtual machine (the guest) will be accessible only from your computer (the host).
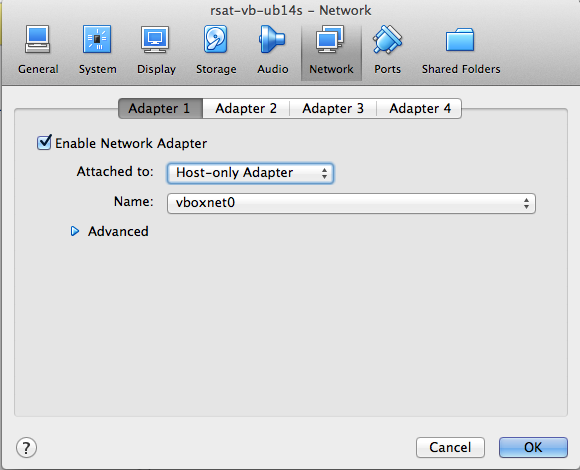
In the panel showing the available virtual machines, right-click on the RSAT-VM (rsat-vm-2018-05), open the Settings … dialog box. In the tab Network, select Adapter 1, check Enable Network Adapter, select Attached to: Host-only Adapter (snapshot).
In the pop-up menu besides the option Name, select vboxnet0.
 ]
]
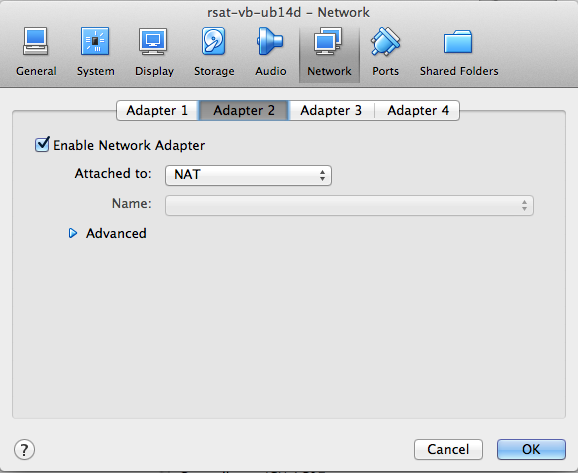
4.2.2 NAT
Note: the host-only adapter will enable you to establish a connection (Web browsing, ssh connection) from the hosting operating system (the usual environment of your computer) to the guest system (the virtual machine). however, this adapter does not allow to connect the external world from the guest. It is this useful to combine the host-only network (to see your server from your host) and the NAT network (to see the external world from your RSAT VM).
In parallel to the host-only adapter, we thus recommend to enable the second adapter and select NAT (snapshot)..
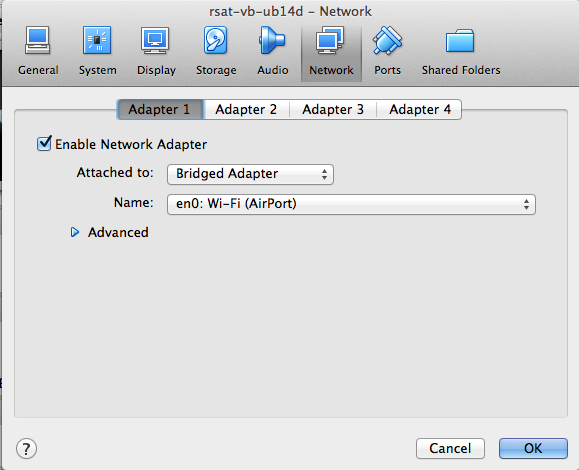
4.2.3 Bridged network
Alternatively , for the sake of flexibility, you might consider to use a bridged network. The bridged adapter is the most convenient, because it establishes a bidirectional connection between your VM (the guest) and the network. Your guest RSAT Web server can thus be used from any other computer in your network. This configuration can typically be usd to make an RSAT server available for all people from the same lab or institute.
Attention! The bridged network makes your virtual machine visible for all the other computers of the local network the host machine (your PC). Check with your system administrator that this fits the local security requirements.
In the panel showing the available virtual machines, right-click on the RSAT-VM (rsat-vm-2018-05), open the Settings … dialog box.
In the tab Network, select Adapter 1, check Enable Network Adapter, select Attached to: Bridge adapter.
In the pop-up menu besides the option Name, select an adapter depending on your local network configuration, e.g. Wi-fi (Airport) (snapshot).
If you are connected to Internet via an Ethernet cable, you can leave the other parameters unchanged.
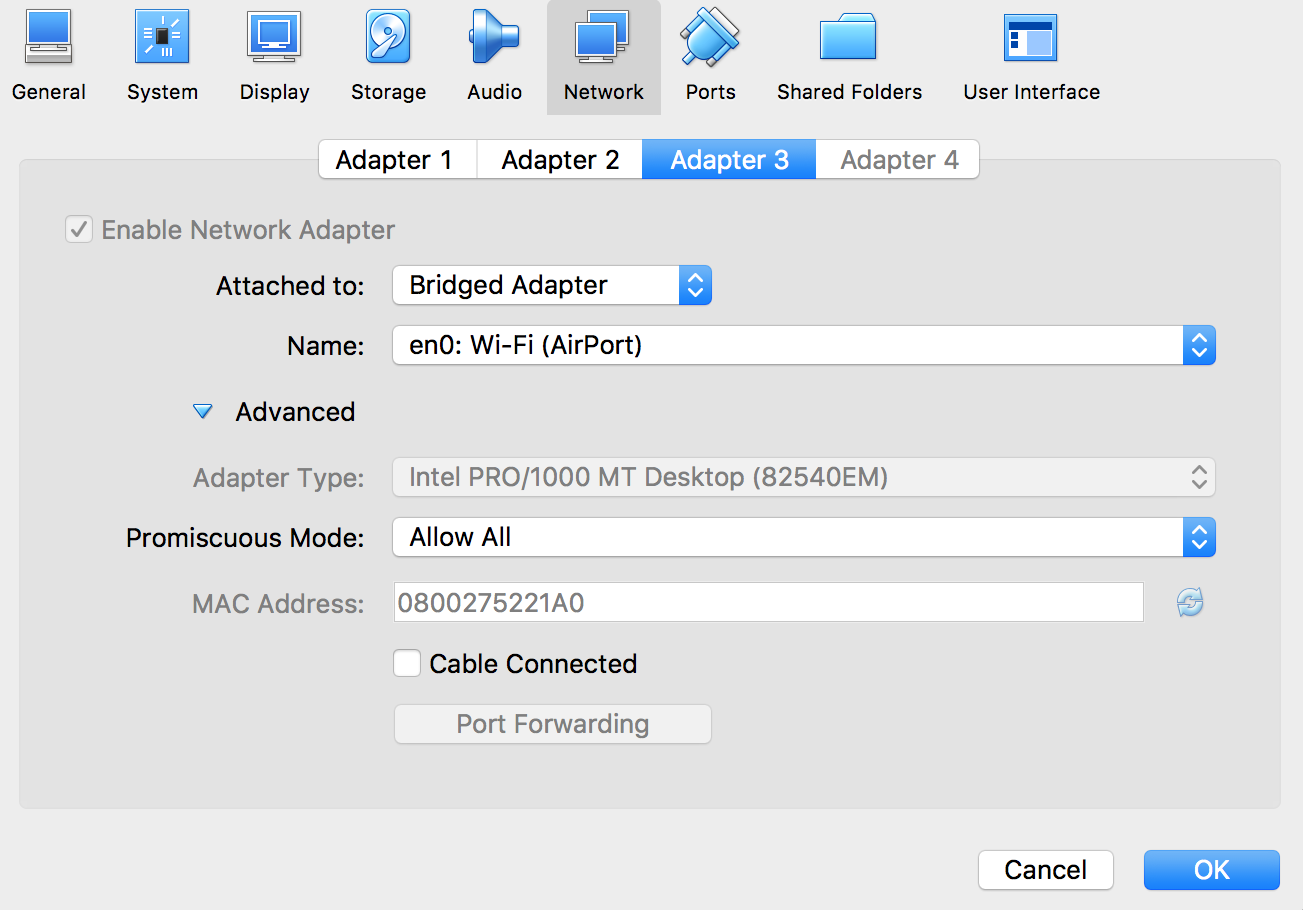
If you are connected via Wi-Fi (wireless), you may need to set up advanced option for Wi-Fi connection.
- In the parameter panel of the bridged network adapter, click Advanced.
- Select Allow all for the Promiscuous mode.
- Uncheck the option cable connected (not sure this is required, but seems reasonable to disactivate cable for a wireless connection).
5 Running RSAT-VM
5.1 Starting the RSAT virtual machine
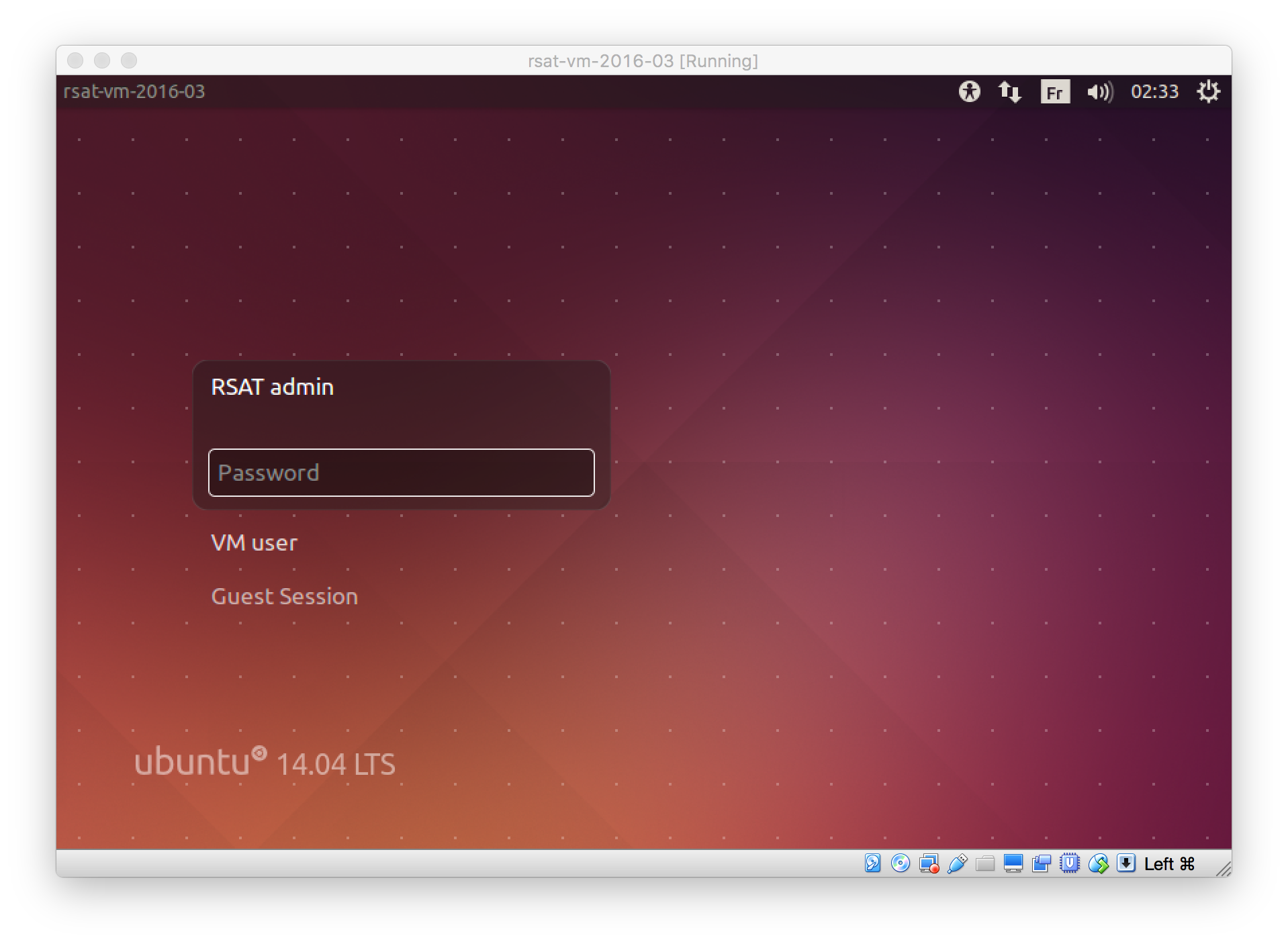
In the left panel of VirtualBox, select the virual machine (rsat-vm-2018-05), and click on the Start icon.
This will open a new window (snapshot).
From now on, your RSAT Virtual Machine is up and running. You can access it in various ways:
- As a Web server
- As a fully functional Linux Desktop server
- On the command line
- As SOAP/WSDL Web services (advanced use).
5.2 Using RSAT-VM as Web server
Open a connection to http://192.168.56.101/ in your web browser.
Note: this IP address is assigned dynamically by VirtualBox. If you already have one or more virtual machines, the last number may take a higher value (e.g. http://192.168.56.102, http://192.168.56.103/).
5.3 RSAT users
RSAT-VM is delivered with two default users, which enable to use the VM as an internal user, either in a terminal (via an ssh connection) or on a fully functional Linux Desktop (graphical environment).
- vmuser enables to use the tools as a normal account on the VM
- rsat is the administrator of the RSAT package, it has the rights to install genomes and modify the code.
Note: the initial password has been
set to tochng for bot users. At your first login you will
be forced to change this password. After having reset your password, you
will be brought back to the terminal of your computer, and you need to
re-type the ssh command in order to actually log in.
5.4 Accessing your RSAT VM via ssh (Unix terminal)
If you are familiar with the Unix command-line environment, you can access your virtual machine from a terminal of the host machine, with the following commands.
- To log in as normal user:
ssh vmuser@192.168.56.101- To log in as RSAT administrator (e.g. to manage genomes):
ssh rsat@192.168.56.1015.5 Using your RSAT VM as a Linux Desktop server (graphical environment)
You can also use the VirtualBox virtual machine through the Linux
Desktop server interface. For this you need to login as either
vmuser (normal user of the RSAT suite) or rsat
user (administration of the tools, genome installations, …).
5.5.1 RSAT-VM log-in
The RSAT VM has two predefined users:
RSAT admin, the owner of the RSAT folder (/packages/rsat). Log in with this account when you need to manage the RSAT installation (modify the code, install additional genomes, …).
- Username: rsat
- Iniitial password: tochng
RSAT VM user, not owner of the RSAT folder. Log in with this account for normal use of the virtual machine (including RSAT suite).
- Username: vmuser
- Initial password: tochng
We intently chose an overly simple temporary password to ensure compatibility with AZERTY as well as QUERTY keyboards, but you will be forced to change your password at first login. It is important to choose a suitable non-trivial password, to prevent hackers from accessing your virtual machine.
Both rsat and vmuser are sudoers. After login, you thus become the master of your Virtual Machine, which allows you to create new users, install packages, etc.
5.5.2 Chosing the adequate keyboard for your computer
A small difficulty when distributing a VM is the large variety of keybords expected to be found on the users’ computers. By default, we selected the standard British QWERTY keyboard.
On the desktop version, click on the Settings icon ![]() , then on the
, then on the ![]() , and check the
keyboard..
, and check the
keyboard..
On Ubuntu server version, keybord configuration can be modified with following command.
sudo dpkg-reconfigure console-data